Showing posts with label schematic. Show all posts
Showing posts with label schematic. Show all posts
Friday, December 12, 2014
Solar Battery Charger Circuit Schematic
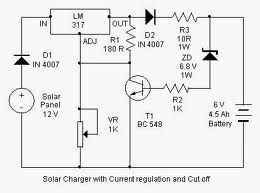
Here is a solar charger circuit that is used to charge Lead Acid or Ni-Cd batteries using the solar energy power. The circuit harvests solar energy to charge a 6 volt 4.5 Ah rechargeable battery for various applications. The charger has Voltage and Current regulation and Over voltage cut off facilities.
Thursday, October 23, 2014
Schematic diagram of a USB player
Usb series player is an electronic device or electronic circuit that functions as an MP3 player that is stored on a storage device such as USB flash.In this usb circuit using an IC as a modifier of digital voice data into analog so that it can be applied to a headphone, or again through the power amlplifier strengthened so that it can be heard through the speakers. IC used in this circuit using IC PCM2902 as a modifier of a digital data into analog data storage.
Below is a schematic diagram of a USB player.
| Schematic usb player |
Saturday, October 18, 2014
Yamaha MFC06 Schematic
Yamaha MFC06 Schematic
Yamaha GigMaker Acoustic Guitar Pack
Yamaha YPG-635 Keyboard Package with Portable Grand Piano ...
The Yamaha mfc06 seems designed specifically ..
Thursday, October 16, 2014
TV audio video transmitter Schematic Diagram
This is a simple TV audio video transmitter circuit can be constructed using this schematic diagram . This TV audio video transmitter circuit can be used to transmit video signals from VCR ( or some other device ) to a TV without using any cable .
Video signals input at jack J1 are first terminated by resistor R6 and coupled through capacitor C1 to clamping-diode D1. Potentiometer R3 is used to set the gain of the video signal; its effect is similar to that of the contrast control on a TV set.
TV audio video transmitter Schematic Diagram
Bias-control R7 can be used to adjust the black level of the picture so that some level of signal is transmitted, even for a totally dark picture.
RF-transformer T1 and its internal capacitor form the tank circuit of a Hartley oscillator thats tuned to 4.5 megahertz. Audio signals input at J2 are coupled to the base of Q3 via C2 and R4: the audio signal modulates the base signal of Q3 to form an audio subcarrier that‚s 4.5-megahertz higher than the video-carrier frequency.
The FM modulated subcarrier is applied to the modulator section through C5 and R9.
Resistor R9 adjusts the level of the subcarrier with respect to the video signal.
Resistor R9 adjusts the level of the subcarrier with respect to the video signal.
Transistors Q1 and Q2 amplitude modulate the video and audio signals onto an RF-carrier signal. The operating frequency is set by coil L4, which is 3.5 turns of 24- gauge enameled wire on a form containing a standard ferrite slug.
The RF output from the oscillator (L4, C7 and C9 ) section is amplified by Q5 and Q6, whose supply voltage comes from the modulator . Antenna matching and low-pass filtering is performed by C12, C13, and L1.
Resistor R12 is optional; it is added to help match the output signal to any kind of antenna.
To align this audio video transmitter you need to tune a TV receiver to an unused channel between 2 and 6. The TV must have an indoor antenna connected directly to it; an outdoor antenna or cable wont work. Make sure both potentiometers (R3, R7) are in middle position and apply power to the transmitter. Adjust L4 with a nonmetallic tool until the TV screen goes blank ,then fine-adjust L4 for the "most-blank" picture.
Connect the video and audio outputs from a VCR(AV source) to jacks J1 and J2 (respectively) of the transmitter .
After that you should see a picture on the TV screen: if you do, readjust L4 for the best picture; if you dont, check the board for any bad connections. Next, adjust R3 for the best picture brightness and R7 for the best overall picture.
Finally, adjust T1 with a nonmetallic tool for the best sound .
The TV transmitter combines line level audio and video signals, and transmits the resulting signal up to 300 feet. The circuit can be powered from a 9-12V power supply circuit .
Wednesday, September 3, 2014
harman kardon DVD 25 SMPS SCHEMATIC Wiring diagram Schematic NDV8501 NDV8601
harman/kardon NDV8501 / NDV8601 Based Progressive Scan DVD Player
Model Number: DVD25
Compactable with CD as well as DVD with Region Code ‘0’ or ‘2’

SMPS SCHEMATIC [Click on the pictures to Zoom In]


To reset the unit
* Set the unit in SY-BY.
* Push “Clear” button on the remote control, until the unit Power ON. [This will not change the Zone]
To read the software version.
* Set the unit in ON mode.
* Push Set-up button on the remote control.
* Push ‘1211’, and then a new menu showing the data of the unit.
To Exit, push Set-up.
Friday, August 29, 2014
IC LA78040 schematic for vertical deflection
Synchronization circuit to make the signals useful in the process of scanning of the transmitter and sent to the Vertical and Horizontal. To be able to produce images on the picture tube phosphor surface is the same as what was sent, then the necessary adjustments to correct with ualsan which has decomposed on the sender and receiver on the review must be made again, and this is called synchronization.
 |
| Click to view larger |
On TV transmitter switching pulses that have made the same frequency as in the reviewing, and by using the switching pulse is then mulapenguilasan point getter on the tube and picture tube can be adjusted simultaneously.
At the transmitter, each end of the line reviews one pulse is emitted horizontally, and also at each end of the line vertical review (this is called a field review), another pulse is emitted. At the receiver using switching pulses had the time of the beginning (start) review can be arranged horizontally and vertically. Switching pulses are called the horizontal synchronizing signal and vertical synchronization.Vertical SynchronizationA. Vertical in the tv series has the following functionsa) bend / open beams of light (information) to the vertical direction.b) Synchronize files from a transmitter in the form of images with short time.
Schematic Audio Power Amplifier with IC AN7118S
*notif : this circuit is stereo power amplifier
Although the schematic power amplifier with IC AN7118S is difficult for lees understood making of PCB track . But once tried to design on PCB is not so difficult. Because the actual components close together and easy to design it. This Circuit need minimum voltage 1 volt and maximum voltage 3 volt. It is a low voltage amplifier with power output 2 x 35 m Watt .
Schematic circuit below :
 | ||
| Click to Enlarge |
Components Required :
Resistor / Condensator / Capacitor : 4,7Ohm (2x) , 0,01 uF (2x) , 47uf (2x) , 68 pf (2x) , 1uF (2x) , 22uF (2x) , 220 uF (1x) , 470uf (2x). Condensator / capacitor voltage use 16 volt. Only Condensator on output speaker use voltage 25 volt.
Subwoofer amplifier schematic diagram
Amplifier circuit is very suitable for use in subwoofer speaker, because its strong. This circuit using ic, ic based on STK. to use it can be used on cars that use speakers or a subwoofer system in his car. 30 V supply voltage that has been rectified. Power output 20W mono.
Part List :
R1 = 100K
R2 = 47R
R3 = 100R
R4 = 1R
C1 = 220uF
C2 = 100uF
C3 = 100uF
C5 = 10uF
C6 = 1uF
C7 = 1uF
C8 = 1000uF
C9 = 0.1uF
IC = STK011 , STK015 , STK016
Wednesday, August 27, 2014
TDA7240 TDA7241 amplifier schematic
On this circuit based at IC TDA7240A , this circuit require minimum voltage 8 volt and maximum voltage 18 volt DC. Max power output 40 Watt with 4 Ohm impedance. this circuit can use to Amplifiy the audio device. See the circuit schematic below :

Sunday, August 24, 2014
New Photo Meter Assesses Ambient Light Schematic
Most PN-junction diodes can be used as photodiodes. While not optimized for this application, they do work. When the diode is reverse biased, it will produce a small photovoltaic output as the light level is increased. LEDs are particularly suited for this task because their housings are transparent.
You can construct a simple schema that will assess the condition of ambient lighting and, because many LEDs’ packages are tinted to enhance their emitted color, may even yield a reasonable evaluation of the detected color. The results are not as effective as those obtained using a high-quality optical filter, which typically has narrow bandpass characteristics, but they can be quite acceptable. Though the design described here does not produce the accuracy of designs with laboratory-grade photodetectors and transimpedance amplifiers, it can be quickly assembled and will produce usable results at a low cost.
Three LEDs are used; experimentation will indicate which device has the best sensitivity to which color (Figure 1). The ambient light falling on the LEDs causes some current flow—typically in the range of 10 to 100 nA—through each LED, depending on the applied illumination level. This current flows through the base of a transistor, Q1, and is amplified. Q1’s collector current then splits between potentiometer R4, which acts as a first-stage gain calibration, and the base of Q2.
Photo Meter Assesses Ambient Light Schematic
You can construct a simple schema that will assess the condition of ambient lighting and, because many LEDs’ packages are tinted to enhance their emitted color, may even yield a reasonable evaluation of the detected color. The results are not as effective as those obtained using a high-quality optical filter, which typically has narrow bandpass characteristics, but they can be quite acceptable. Though the design described here does not produce the accuracy of designs with laboratory-grade photodetectors and transimpedance amplifiers, it can be quickly assembled and will produce usable results at a low cost.
Three LEDs are used; experimentation will indicate which device has the best sensitivity to which color (Figure 1). The ambient light falling on the LEDs causes some current flow—typically in the range of 10 to 100 nA—through each LED, depending on the applied illumination level. This current flows through the base of a transistor, Q1, and is amplified. Q1’s collector current then splits between potentiometer R4, which acts as a first-stage gain calibration, and the base of Q2.
Photo Meter Assesses Ambient Light Schematic

Q2 provides further amplification and drives the left side of a bridge schema (D1A and D1B). Note that R2/D1 and R3/D2 form a balanced bridge. Q2’s collector current provides a slight imbalance to the bridge. The meter, M, measures this imbalance. R5 adjusts the sensitivity of the meter. Set R4 and R5 such that the meter has an appropriate deflection. R4 is useful for selecting the quiescent point; R5 is useful for adjusting the sensitivity.
Before building the schema, check whether the LEDs can be used as photo sensors. To determine whether a given LED is a good photodiode, check the voltage across the LED using a common digital multimeter set to its most sensitive range—typically 200 mV. Typical output voltage should be approximately 0.3 to 1 mV with typical office illumination.
Thursday, August 21, 2014
0 15Watt amplifier schematic
Amplifier circuit is also very suitable when used in fm radio receiver. Supply voltage required 8 - 25 Volt DC with a maximum output power 0.15W.See Schematic below.Part List
R1 = 100R
C1 = 1nF
C2 = 4.7uF
C3 = 10uF
C4 = 100uF
C5 = 47uF
C6 = 4.7nF
U1 = TA7066
Monday, August 18, 2014
FM Radio Transmitter schematic with pcb
For those of you like / love to talk in the air can assemble this simple circuit that can be received by the radio receiver to within a few hundred feet. The voice that issues by this circuit at all clear without rustling. Can also be used to link communications over the air using this radio transmitter, provided that other person also had the same circuit.
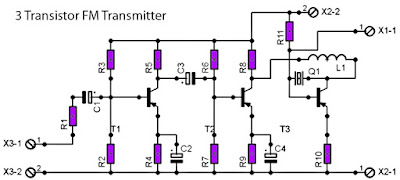
This PCB design :

Description :
Resistor
R1__________________1K
R2__________________18K
R3__________________82K
R4__________________1K2
R5__________________5K6
R6__________________39K
R7__________________18K
R8__________________68K
R9__________________470R
R10_________________100R
R11_________________50K
XTal
Q1__________________ Crystal according to the desired frequency
Inductor
L1__________________10uH
Capacitor
C1__________________10uF
C2__________________30uF
C3__________________20uF
C4__________________47uF
Transistor
Tr1_________________2SB175
Tr2_________________2SB175
Tr3_________________2SB178
Antenna
X1-1________________10-20 meters
Connector
X2-1________________Ground
X2-2________________VCC 9-12 Volts DC
X3-1________________Input
X3-2________________Ground
Saturday, August 16, 2014
300W subwoofer amplifier schematic
 This is an amplifier circuit that is formed from a transistor amplifier miraculous. This circuit is used in the speaker subwoofer with 300W maximum power on each side. To apply it, can be used in the room that is not too large, like the car. And the voltage needed between 25 to 42 Volt DC.
This is an amplifier circuit that is formed from a transistor amplifier miraculous. This circuit is used in the speaker subwoofer with 300W maximum power on each side. To apply it, can be used in the room that is not too large, like the car. And the voltage needed between 25 to 42 Volt DC.This is schematic of 300W subwoofer amplifier

Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
